How To Find A Bond's Coupon Rate
What is the Coupon Charge per unit of a Bond?
Coupon Charge per unit is mostly applied to bonds and it is usually the ROI (charge per unit of interest) that is paid on the face value of a bond by the issuers of bond and information technology is also used to calculate the repayment amount that is made by GIS (guaranteed income security).
Formula
The coupon rate of a bond can exist calculated by dividing the sum of the annual coupon payments by the par value of the bail and multiplied by 100%. Therefore, the rate of a bond tin as well be seen equally the amount of interest paid per year as a percentage of the face value or par value of the bond. Mathematically, it is represented as,
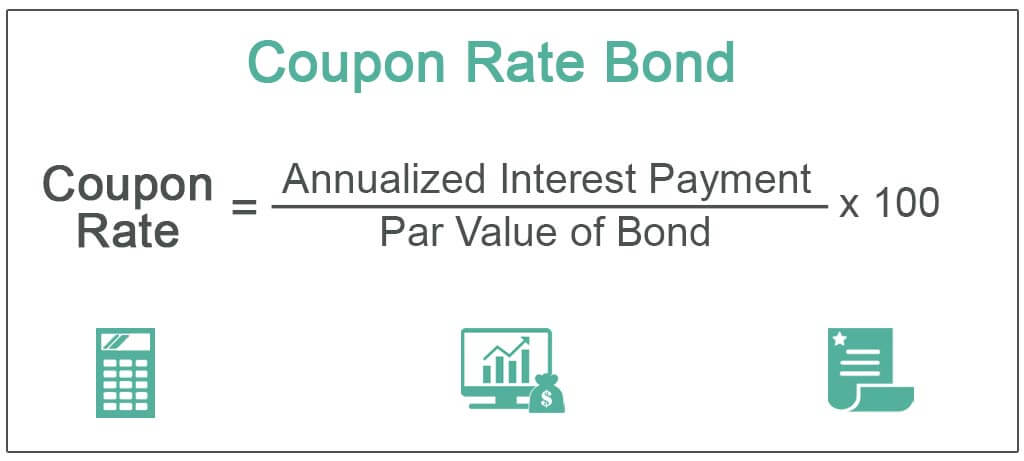
Coupon Rate = Annualized Interest Payment / Par Value of Bond * 100%
You are complimentary to use this image on your website, templates etc, Delight provide us with an attribution link Commodity Link to exist Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Coupon Rate of a Bond (wallstreetmojo.com)
The bond cost varies based on the coupon rate and the prevailing market rate of interest. If the coupon charge per unit is lower than the market involvement rate, and so the bond is said to be traded at a discount, while the bond is said to be traded at a premium if the coupon rate is college than the market involvement rate. Notwithstanding, the bail is said to be traded at par if the coupon rate is equal to the market interest rate
Steps to Calculate the Bond's Coupon Rate
The steps to calculate the coupon rate of a bond are the following:
- Firstly, the face value or par value of the bond issuance is adamant as per the funding requirement of the visitor.
- Now, the number of involvement paid during the yr is determined, and then the annualized interest payment is calculated by adding up all the payments during the twelvemonth.
Almanac interest payment = Periodic interest payment * No. of payments in a year. - Finally, the formula of the coupon charge per unit of the bond is calculated by dividing the annualized interest payments by the par value of the bond and multiplied by 100%, as shown below.
Examples
Let usa take the example of a bond with quarterly coupon payments. Let the states presume a visitor XYZ Ltd has issued a bond having a face value of $i,000 and quarterly interest payments of $15.
- If the prevailing market rate of involvement is seven%, then the bond volition exist traded at _______
- If the prevailing marketplace rate of interest is 6%, so the bond will be traded at _______
- If the prevailing market rate of interest is 5%, then the bond will be traded at _______
As per the given question,
Par value of bail = $1,000
Annual interest payment = 4 * Quarterly interest payment
- = 4 * $15
- = $60
Therefore, the coupon rate of the bond can be calculated using the higher up formula as,

- Since the coupon (6%) is lower than the market interest (7%), the bond volition exist traded at a discount A discount bail is one that is issued for less than its face value. Information technology also refers to bonds whose coupon rates are lower than the market place interest charge per unit and thus trade for less than their face value in the secondary market. read more .
- Since the coupon (6%) is equal to the market involvement (7%), the bond will be traded at par.
- Since the coupon (six%) is higher than the market place interest (5%), the bond will be traded at a premium.
Drivers of Coupon Rate of a Bond
When a bond is issued in the open up marketplace by a company, it arrives at the optimal coupon charge per unit based on the prevailing rate of involvement in the market to go far competitive. Likewise, the issuer's creditworthiness drives the coupon rate of a bond, i.east., a company rated "B" or beneath past any of the tiptop rating agencies is probable to offer a higher coupon rate than the prevailing market interest charge per unit to counterbalance the boosted credit run a risk Credit adventure is the probability of a loss attributable to the borrower'southward failure to repay the loan or come across debt obligations. Information technology refers to the possibility that the lender may not receive the debt's principal and an interest component, resulting in interrupted greenbacks flow and increased cost of drove. read more than taken by the investors. In brusk, the coupon rate is influenced by the marketplace involvement rates and the issuer's creditworthiness Creditworthiness is a mensurate of judging the loan repayment history of borrowers to define their worth as a debtor who should be extended a futurity credit or not. For case, a defaulter'southward creditworthiness is non very promising, then the lenders may avoid such a debtor out of the fear of losing their money. Creditworthiness applies to people, sovereign states, securities, and other entities whereby the creditors will analyze your creditworthiness earlier getting a new loan. read more than .
Relevance and Uses
Coupon Charge per unit is referred to the stated charge per unit of interest on fixed income Stock-still Income refers to those investments that pay fixed interests and dividends to the investors until maturity. Government and corporate bonds are examples of stock-still income investments. read more than securities such equally bonds. In other words, it is the rate of interest that the bond issuers Bond Issuers are the entities that raise and borrow money from the people who purchase bonds (Bondholders), with the promise of paying periodic interest and repaying the main amount when the bond matures. read more than pay to the bondholders for their investment. It is the periodic rate of interest paid on the bail's face up value to its purchasers. It is to be noted that the coupon rate is calculated based on the bond'southward face up value or par value, but not based on the issue price or market value.
It is quintessential to grasp the concept of the rate because almost all types of bonds pay almanac interest to the bondholder, which is known as the coupon charge per unit. Unlike other financial metrics, the coupon payment in terms of the dollar is fixed over the life of the bail. For case, if a bond with a face up value of $ane,000 offers a coupon rate of five%, then the bail will pay $l to the bondholder until its maturity. The annual interest payment volition continue to remain $50 for the unabridged life of the bail until its maturity date irrespective of the ascension or fall in the marketplace value of the bond.
Another of import facet of the charge per unit is that if the prevailing marketplace interest rate is higher than the rate of the bond, then the toll of the bond is expected to autumn because an investor will exist reluctant to purchase the bond at that face value now, as they can become a meliorate rate of return elsewhere. On the other mitt, if the prevailing market place involvement rate is lower than the coupon charge per unit of the bail, and so the price of the bond is expected to increase because information technology will pay a college return on investment than an investor tin brand by purchasing a similar bond at present, as the coupon charge per unit will exist lower resulting in the in an overall decline in involvement rates.
Recommended Manufactures
This has been a guide to what is Coupon Rate of a Bond and its definition. Here we hash out how to calculate Coupon Charge per unit forth with its formula, examples, and relevance. You lot tin can learn more than about from the following articles –
- What is Coupon Rate Formula?
- Bonds vs. Debentures – Compare
- Bond Pricing Formula – Calculation
- Bond Sinking Fund
- ix Courses
- 37+ Hours
- Total Lifetime Access
- Document of Completion
LEARN More >>
How To Find A Bond's Coupon Rate,
Source: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/coupon-rate-bond/
Posted by: lloydcrent1997.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find A Bond's Coupon Rate"
Post a Comment